Introducing custom roles: Flexible access control for users and groups

Contextual AI now offers custom role-based access control for provisioned throughput customers. Create unlimited roles with granular permissions across agents, datastores, and platform settings, and assign them to individual users or custom groups.
Most platforms limit you to preset roles
AI platforms serve multiple teams with different needs—builders create agents, data engineers populate datastores, end users query agents, and finance teams track costs. But platforms with rigid, preset roles create an impossible choice: grant too much access and risk security breaches, or restrict access too tightly and kill team productivity.
Introducing custom role-based access control
Contextual AI administrators can now create unlimited custom roles—each with its own name, description, and precise permissions across agents, datastores, and administration tools. Users can hold multiple roles, and permissions stack to give them exactly the access they need. This flexible access control delivers:
- Granular security control. Protect sensitive data and settings by giving each team exactly what they need—nothing more, nothing less.
- Operational efficiency at scale. Replace manual permission management with reusable roles that grow with your organization.
- Centralized governance. Maintain a single source of truth for roles, permissions, and access—simplifying audits and compliance.
How it works
All new users start with the default user role according to the principle of least privilege. From there, admins can assign additional default roles or custom roles to grant exactly the permissions each member of your organization needs.
Default roles
| Role | Access |
|---|---|
| User | No permissions – applied to new users by default |
| Power user | Permissions to query all agents and read all datastores |
| Admin | Access to all agents, datastores, and admin tools |
Creating custom roles is straightforward.
Creating custom roles
Navigate to the new "Roles" tab in platform settings and click "Create Role." Define your role name and description—like "Data Scientist," "Data engineer," or really anything you want.
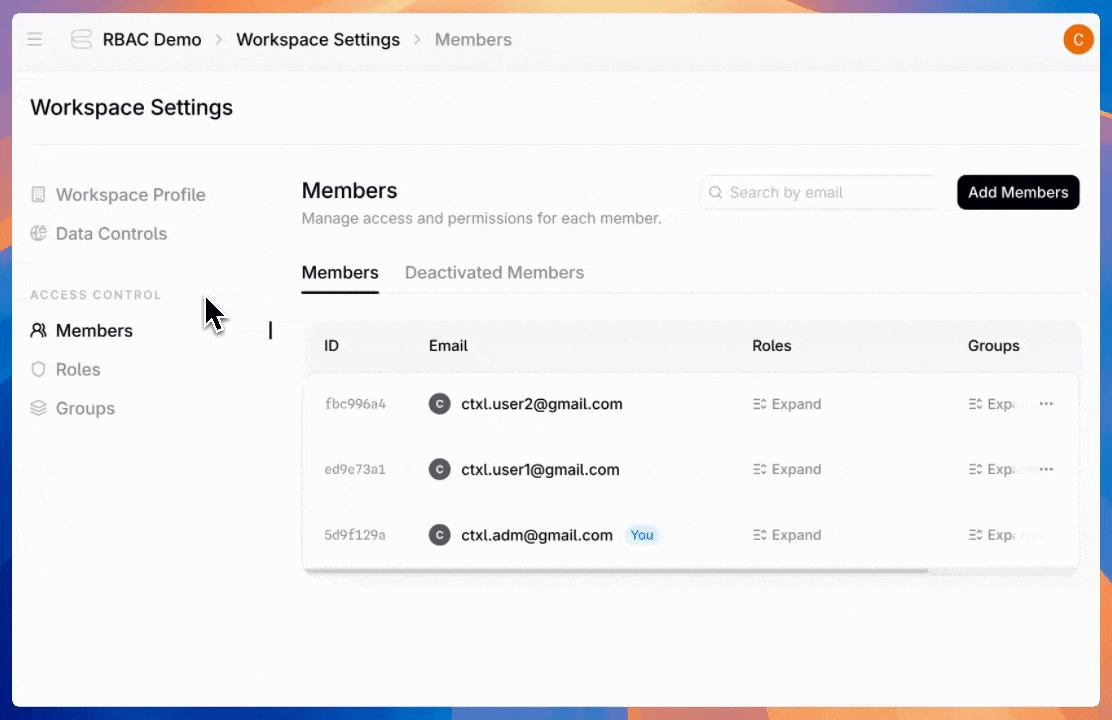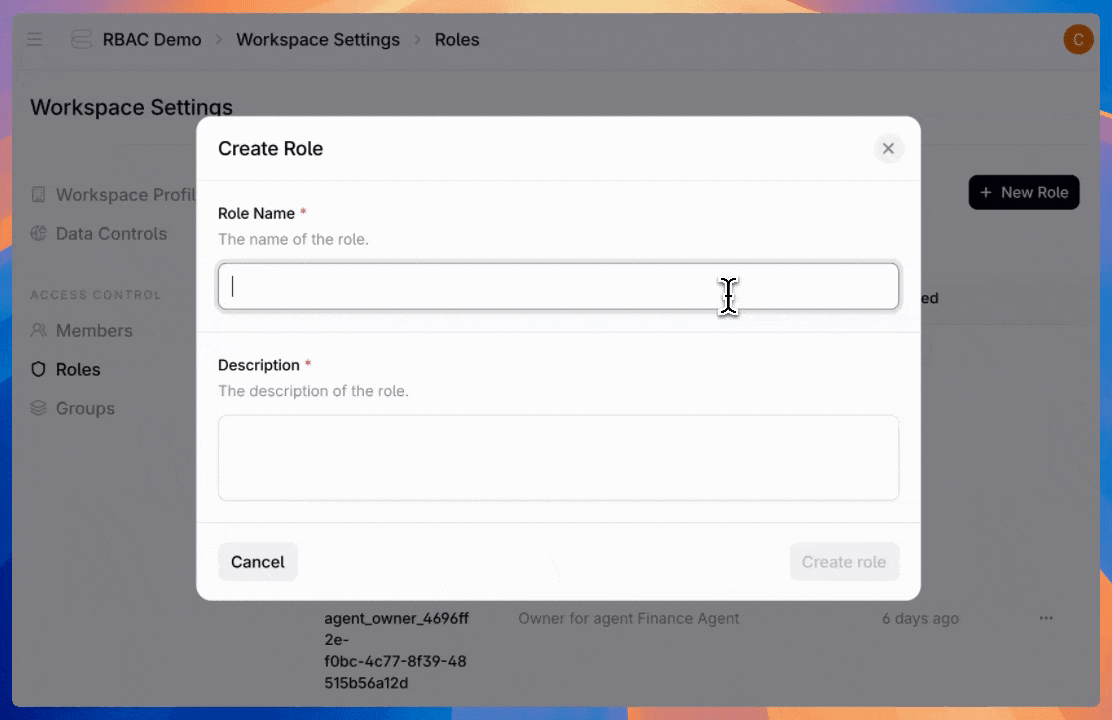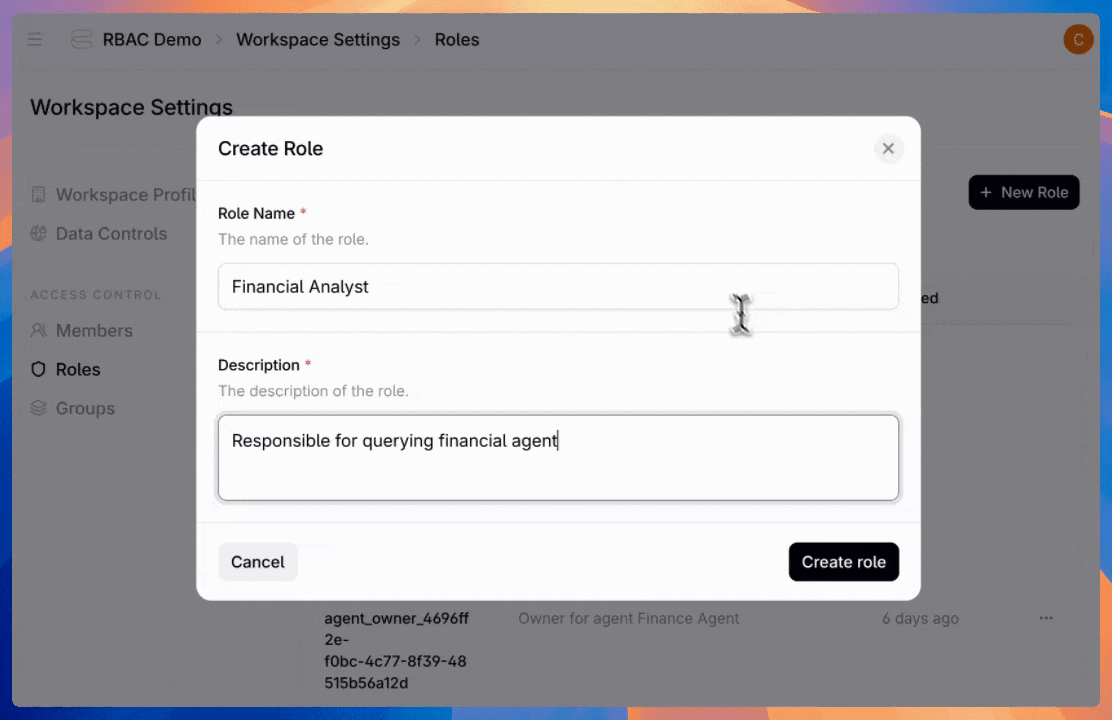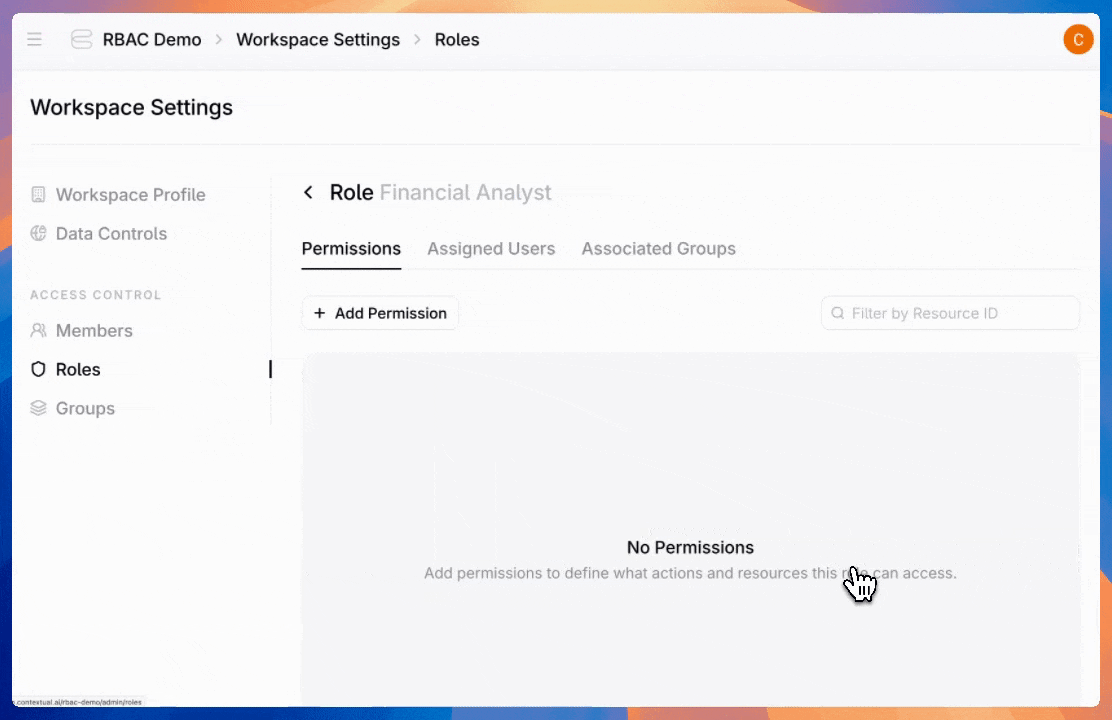
Next, configure permissions for agents, datastores, or admin settings. For each permission type, control the access level—from read-only to full management and creation. Then choose whether access applies to all available entities or just specific ones.
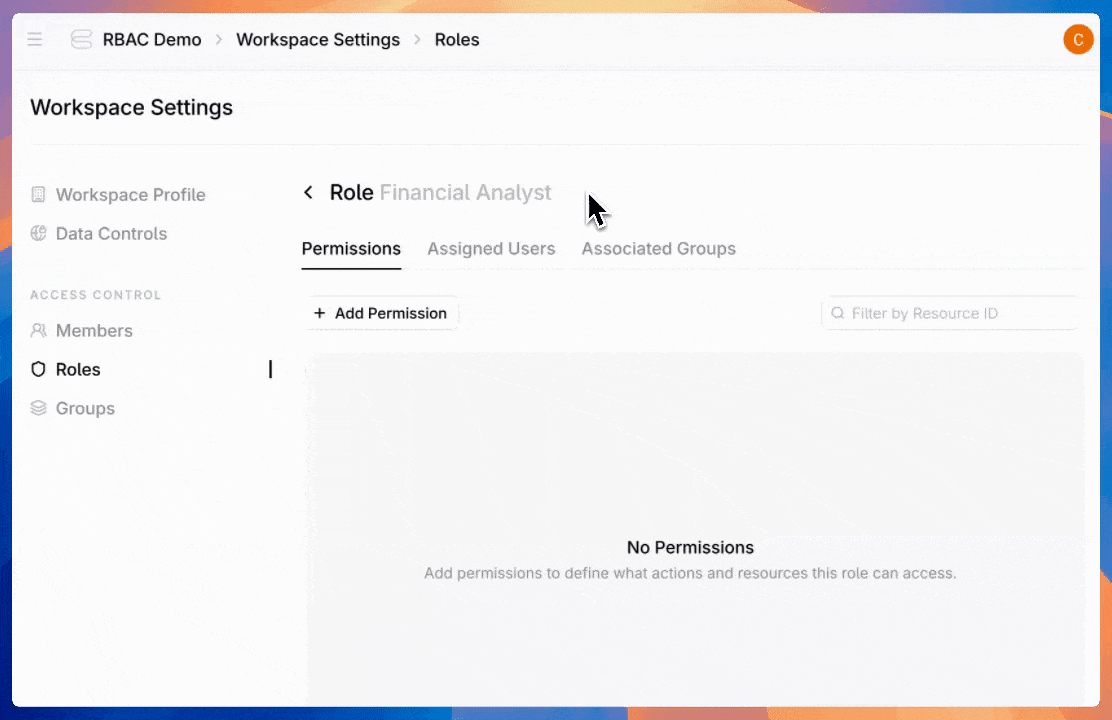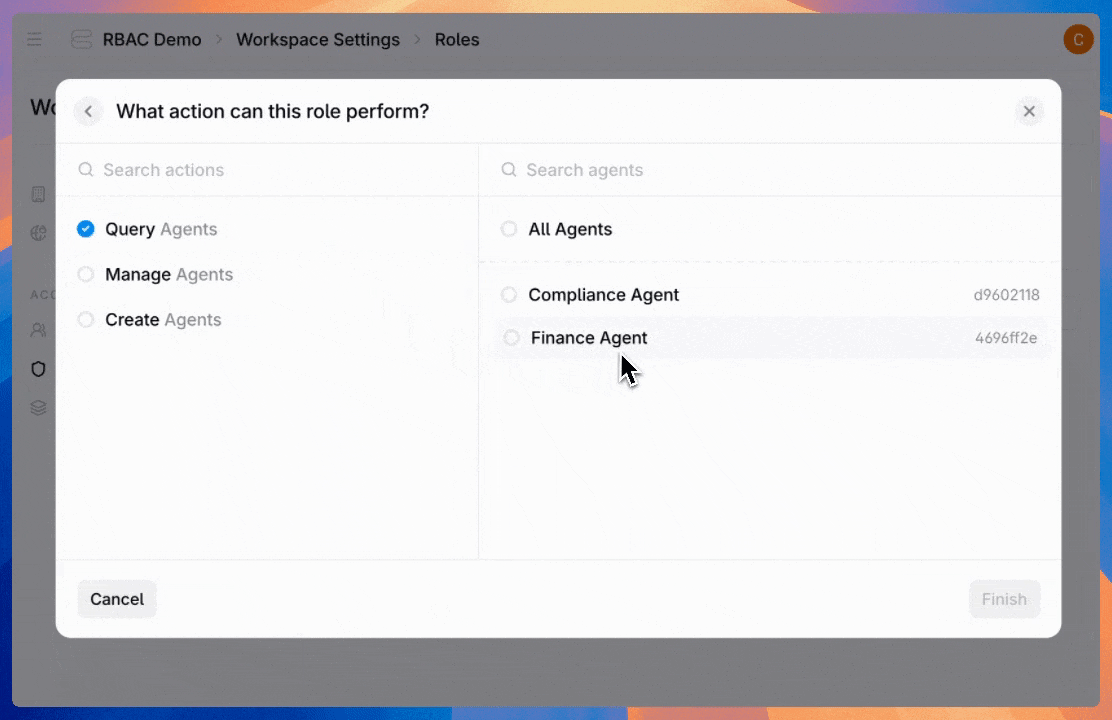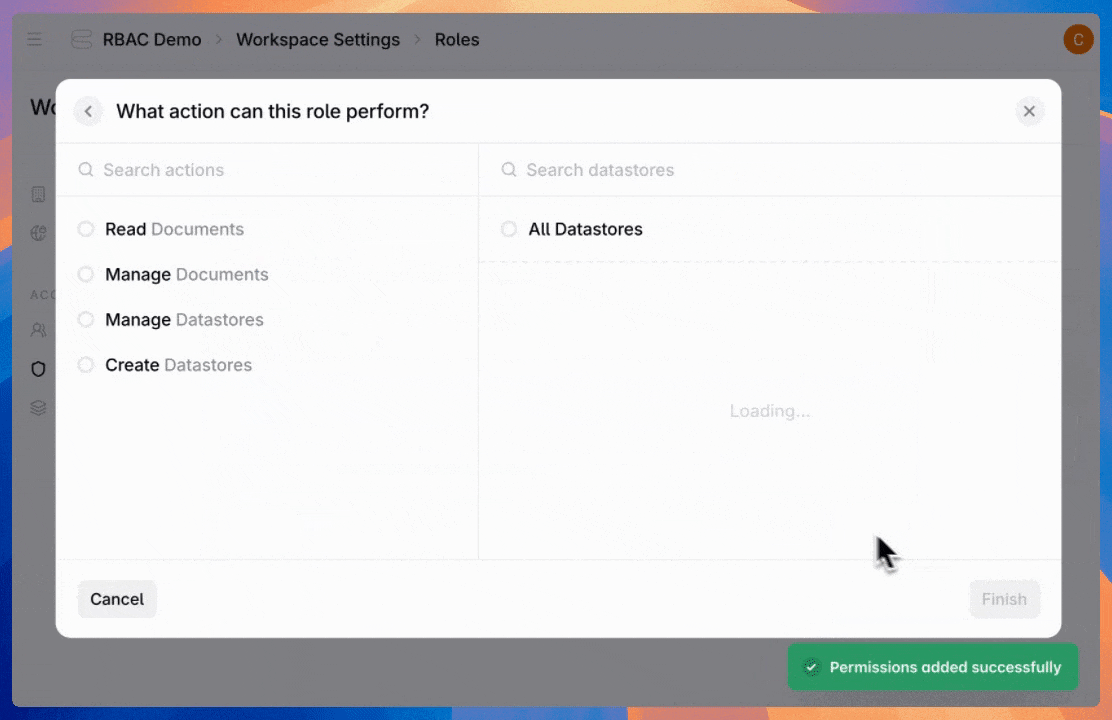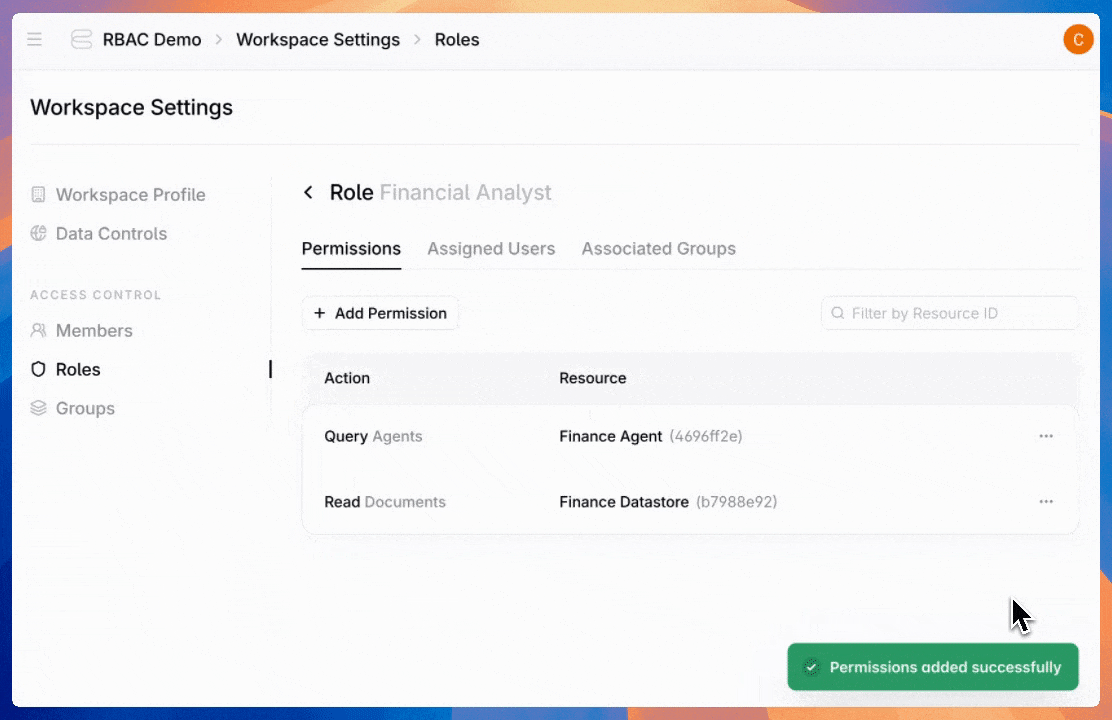
Here are the available permission types:

Assigning roles and creating custom groups
Once you've created roles, assign users to give them the access they need.
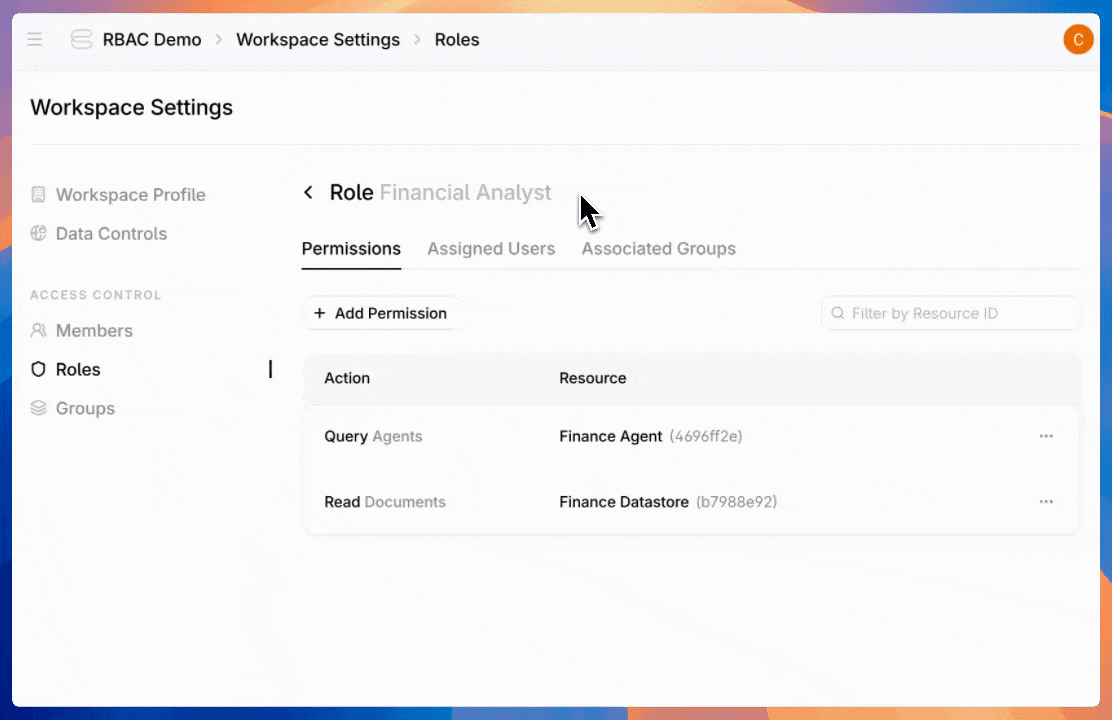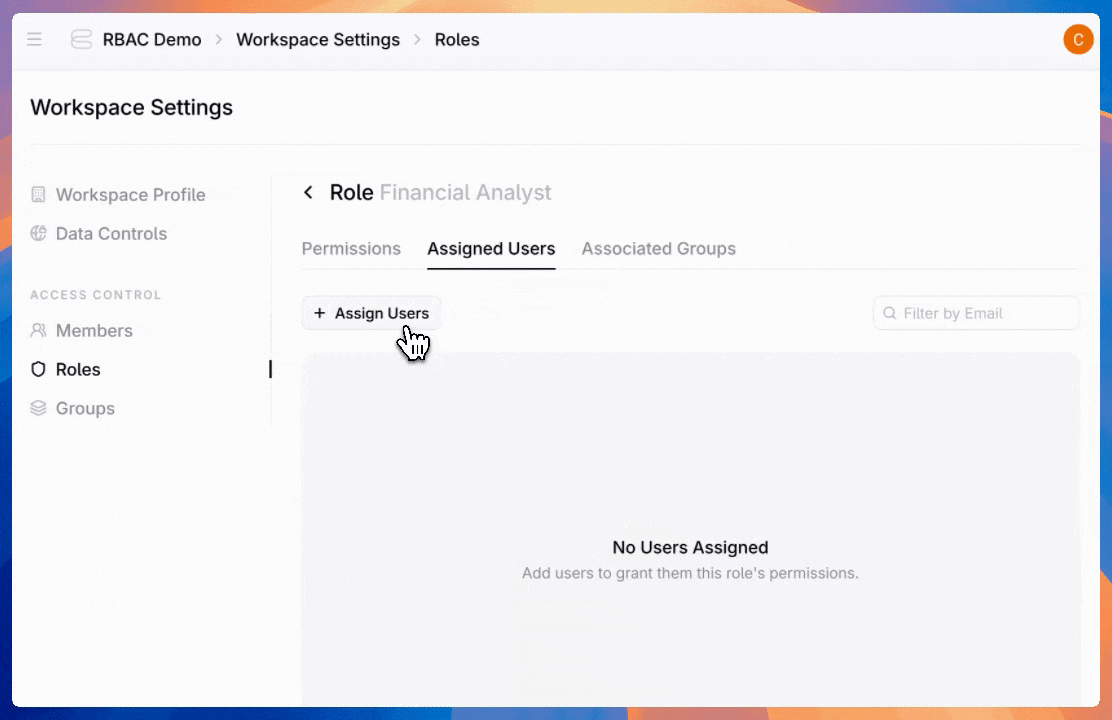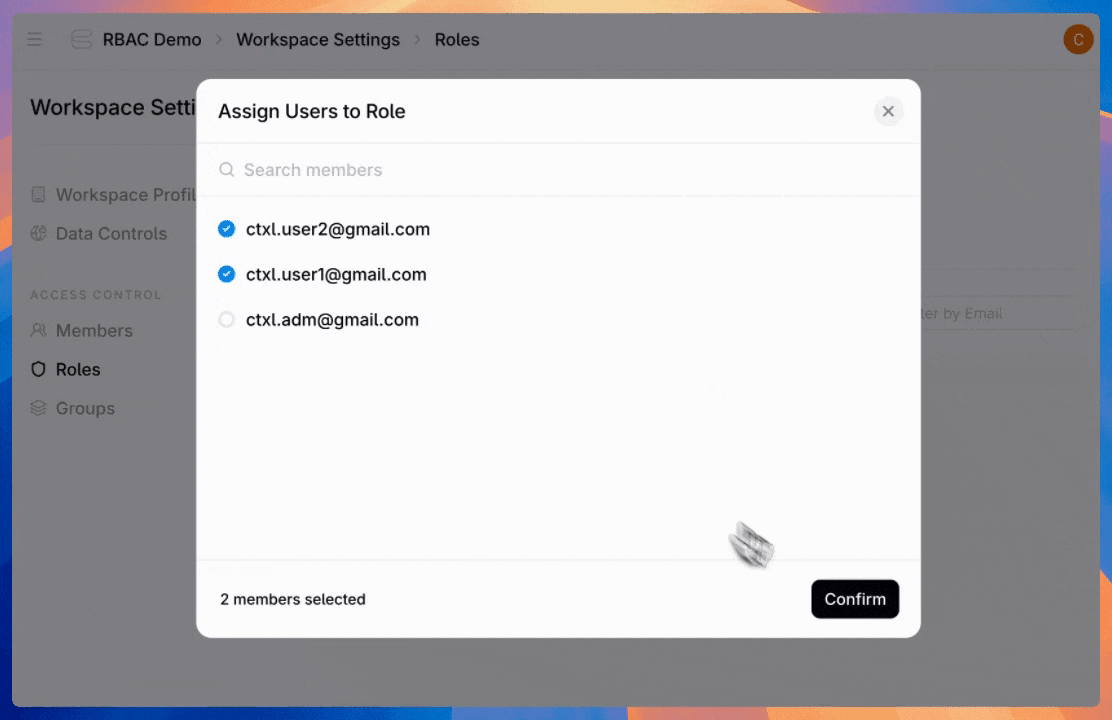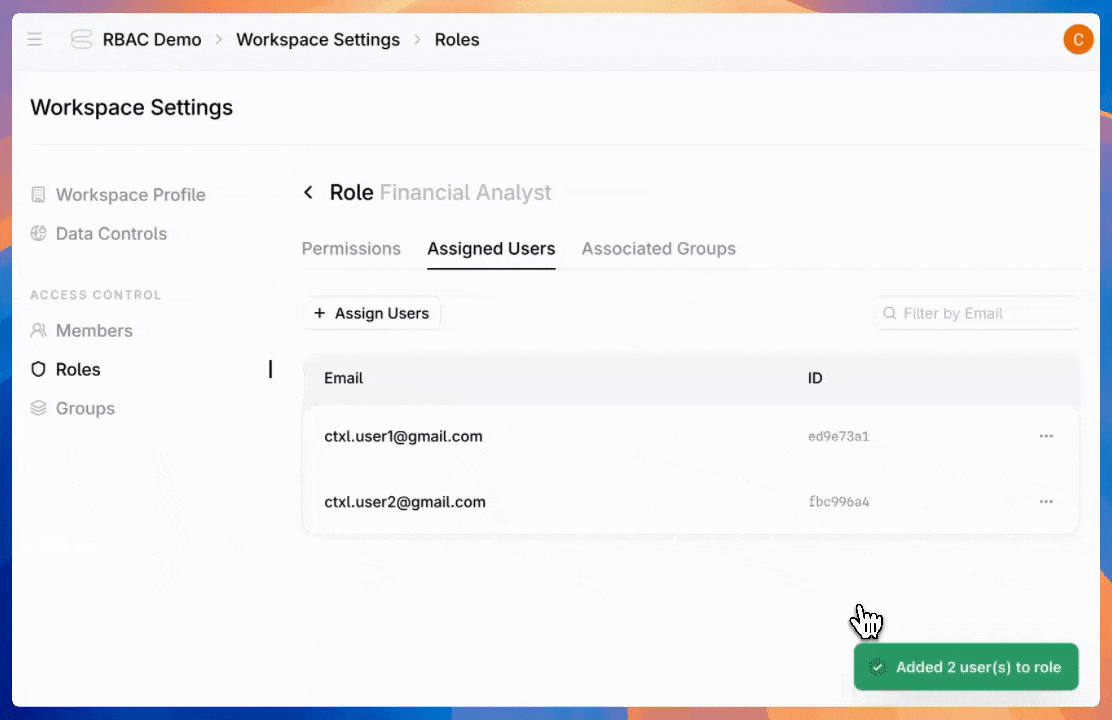
Admins can also create groups—assign a role once to an entire team instead of configuring individual users one by one.
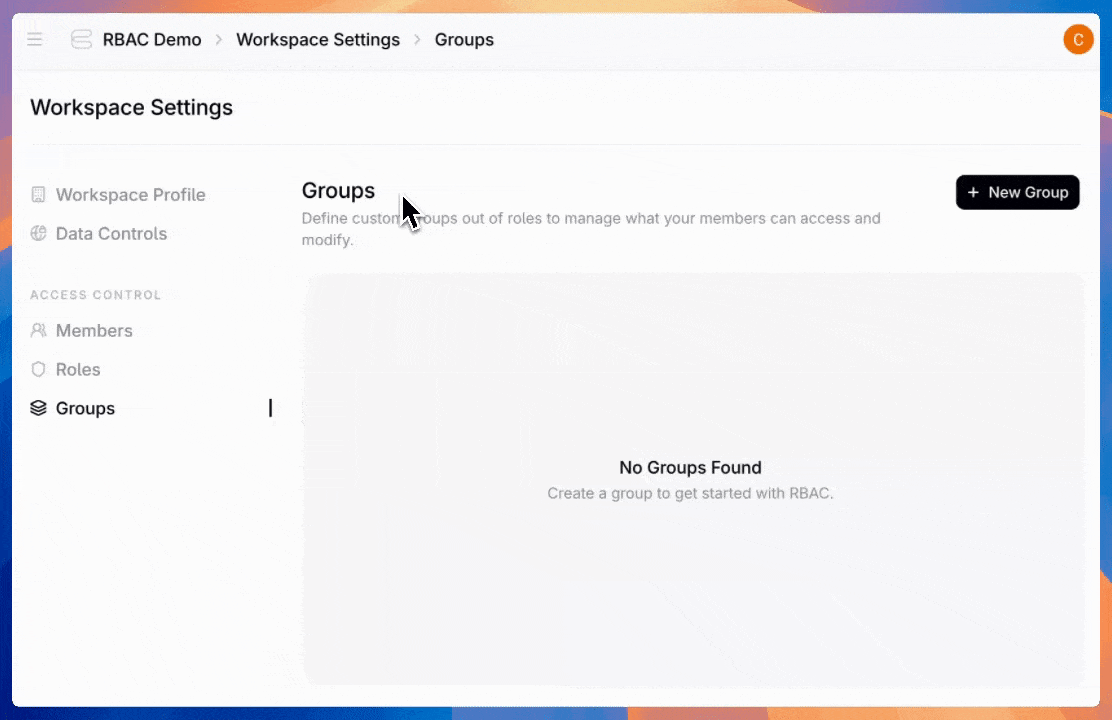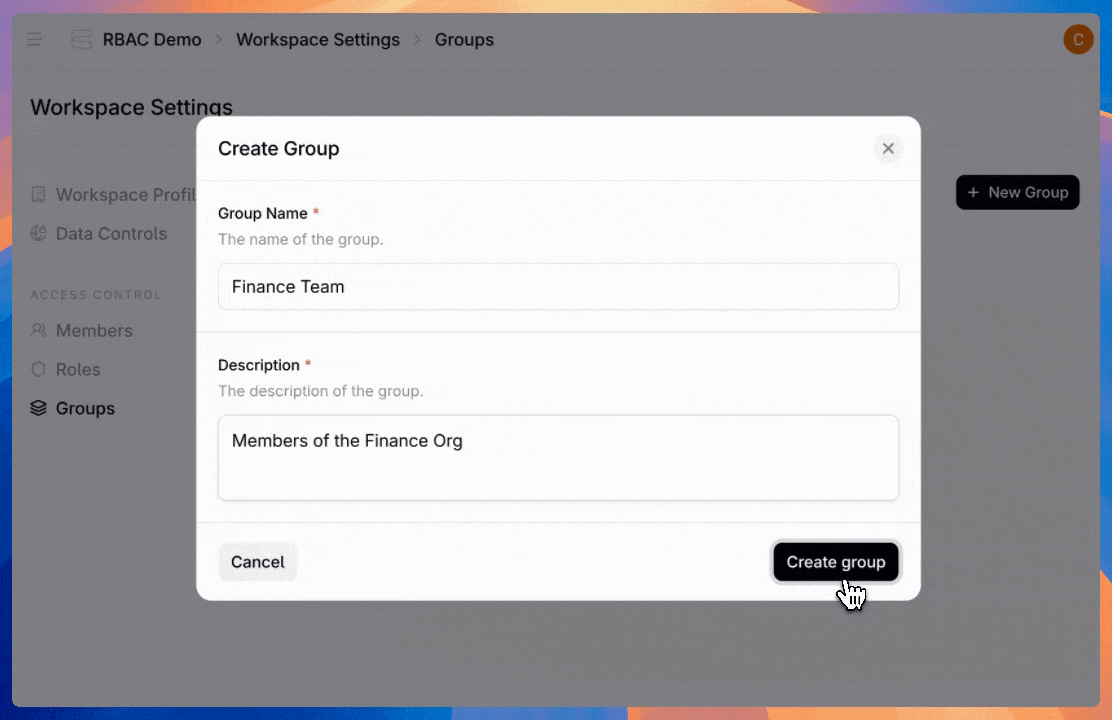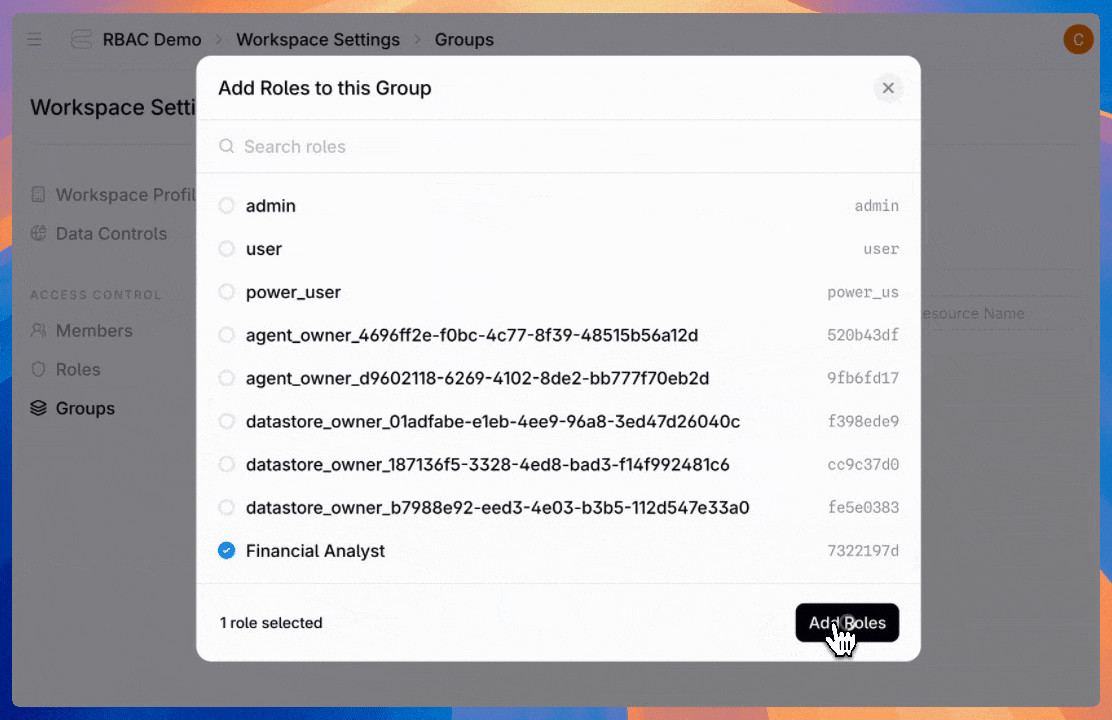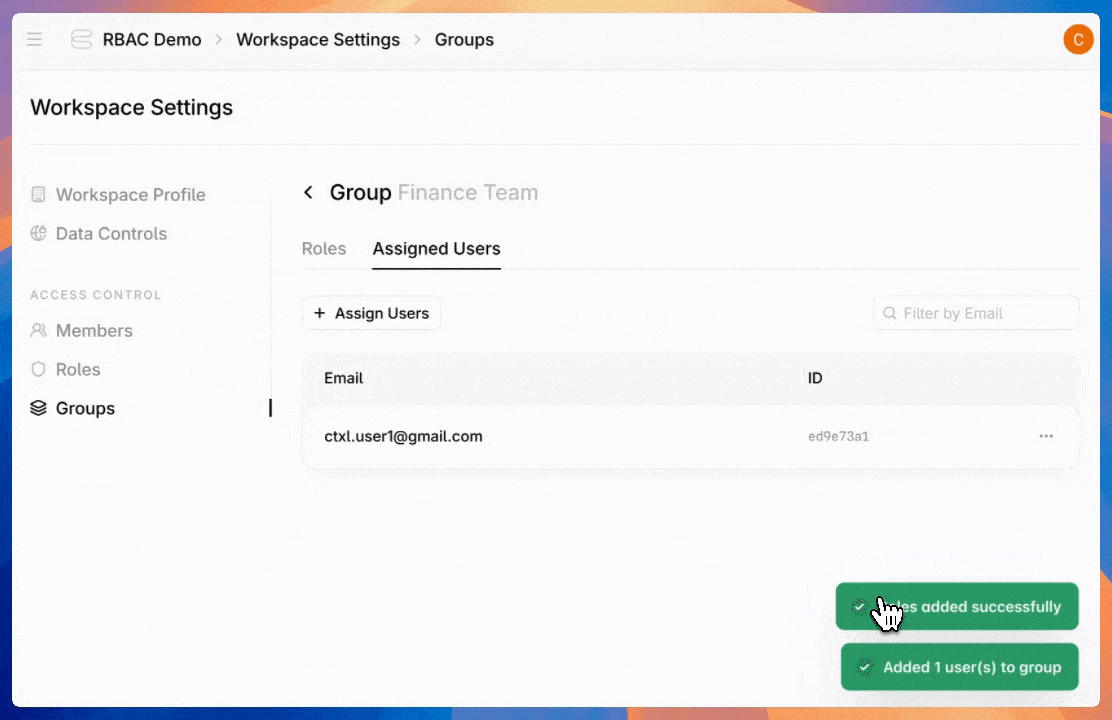
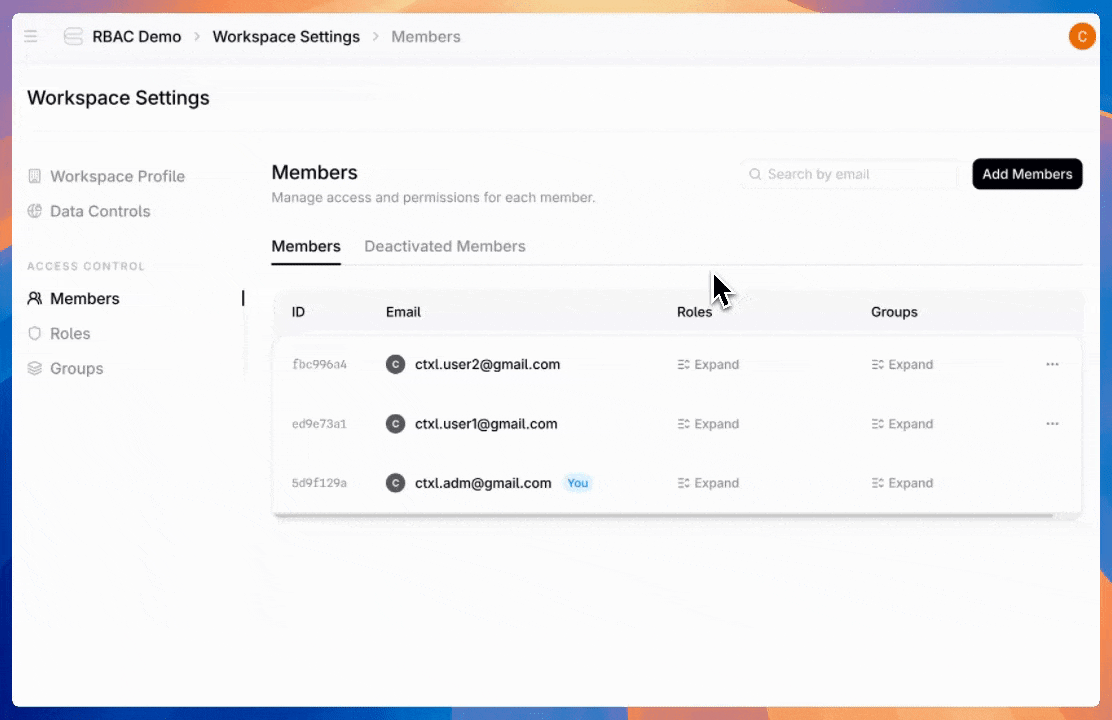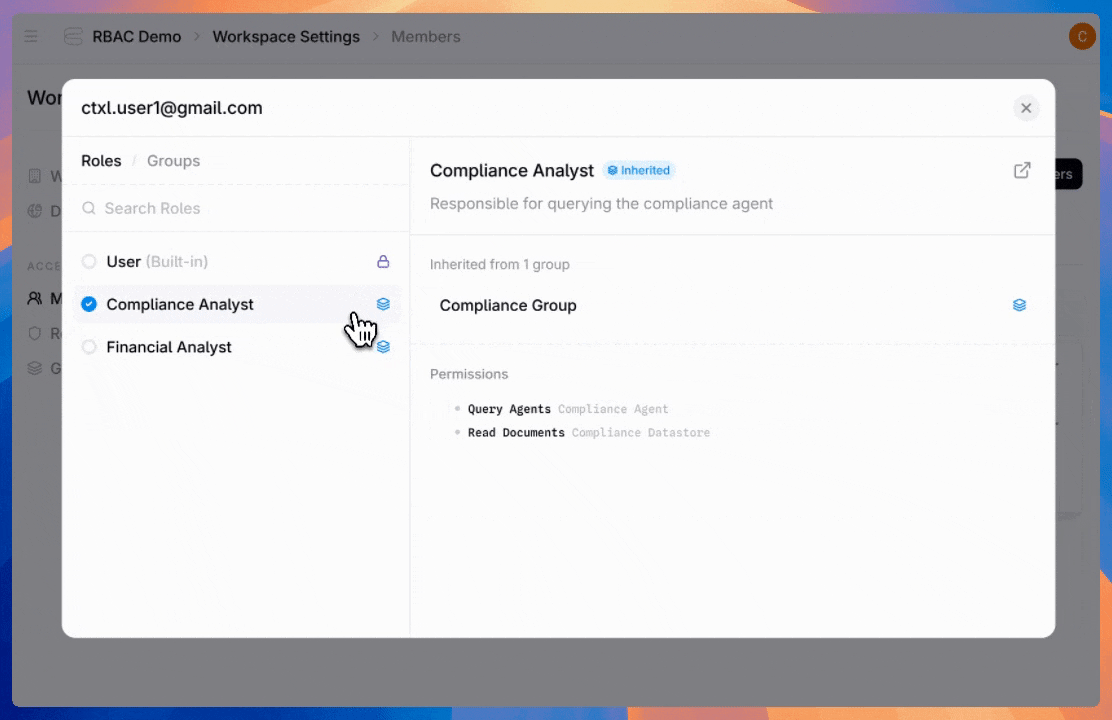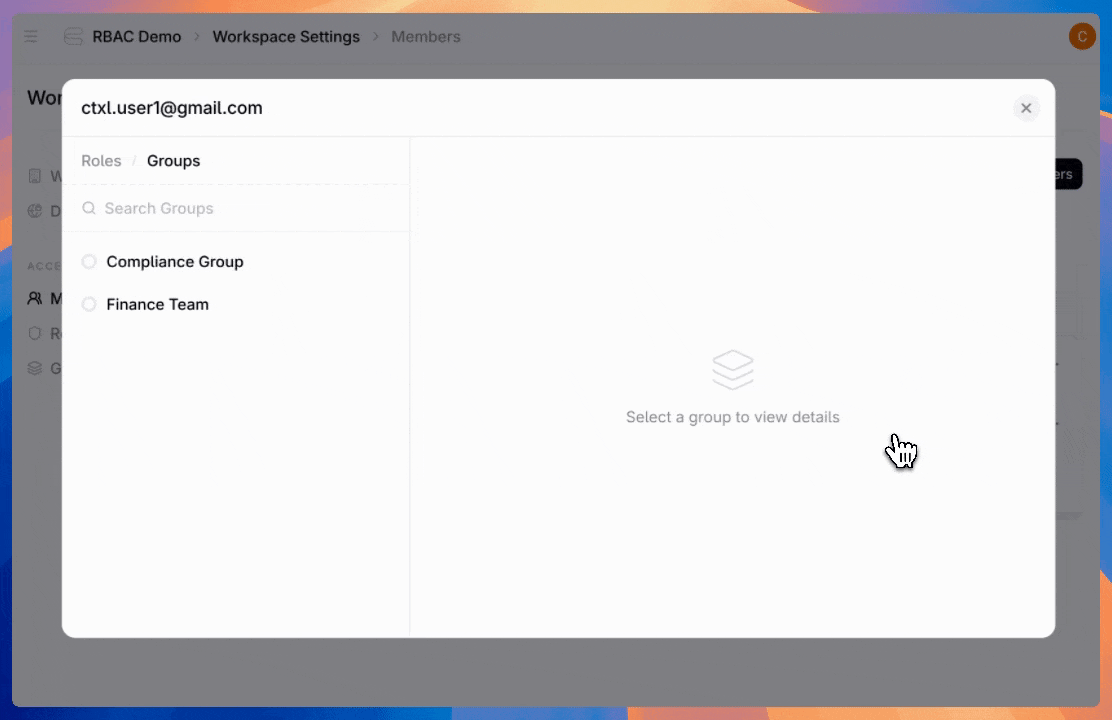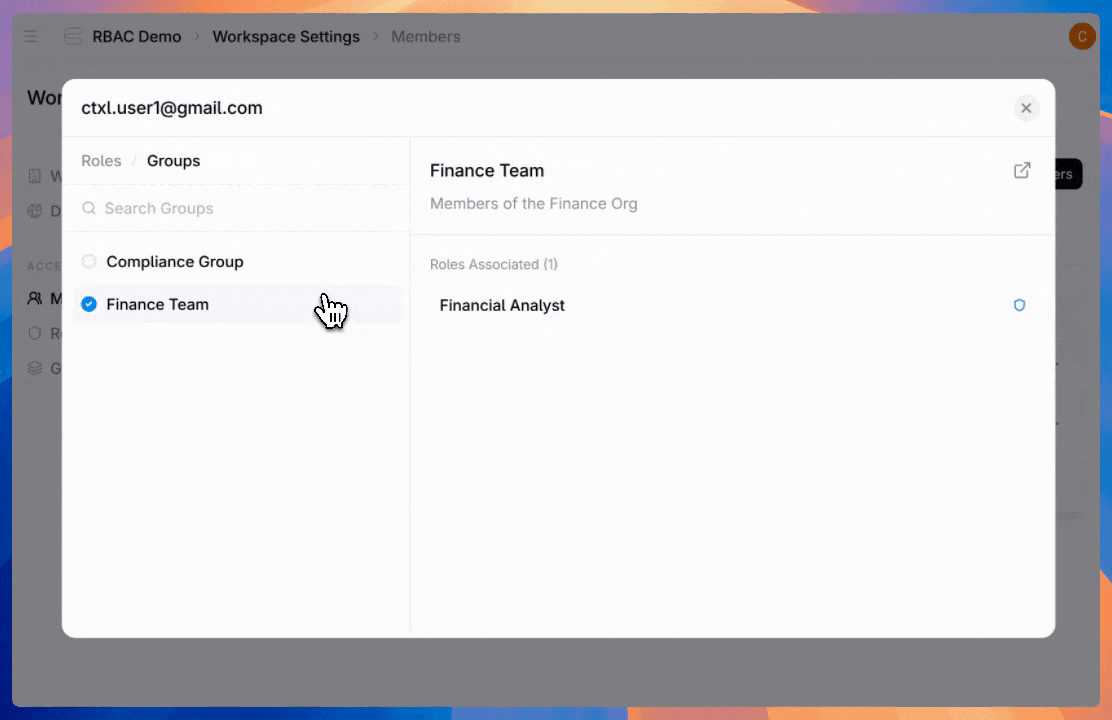
Users can hold multiple roles, and permissions stack. If a user is directly assigned to the “Agent Builder” role and belongs to the “Finance Team” group (which has the “Billing Viewer” role assigned), they get all permissions from both roles.
Admins have full visibility into user roles and groups they belong to, and what permissions they have.
Typical use-cases
Custom roles accommodate any access pattern your organization needs. Here's how a finance organization might structure access:
| Role | Can access | Cannot access |
|---|---|---|
| Billing admin | Billing and usage | Create or manage agents or datastores. Create users or manage feedback |
| Accountant | Query accounting agent | Other agents, Datastores, agent configs, admin tools |
| AI engineer | Create, manage and query all agents, datastores, documents, and feedback | Admin tools |
| Data engineer | Manage “AP Docs” and “SEC filing” datastores | Create, manage or query agents. Admin tools |
| Super admin | Everything | N/a |
Get started today
Custom RBAC is available now to all enterprise customers. Give your teams exactly the access they need—without compromising security. Read the documentation to get started.
Related Articles

Making Search Agents Faster and Smarter
Optimize your search agents for speed and accuracy. Our two-axis approach—reranker improvements and RL-trained planners—reaches 60.7% accuracy.

Introducing Agent Composer—AI for when it IS rocket science
Introducing Agent Composer: Expert AI for complex engineering. Cut hours of specialized, technical work down to minutes.


